The project for Parlormade Scone House was an exciting opportunity to combine our work in photogrammetry with drone SfM (Structure-from-Motion). It also had the increased challenge of capturing narrow in-door spaces through standard photogrammetry.
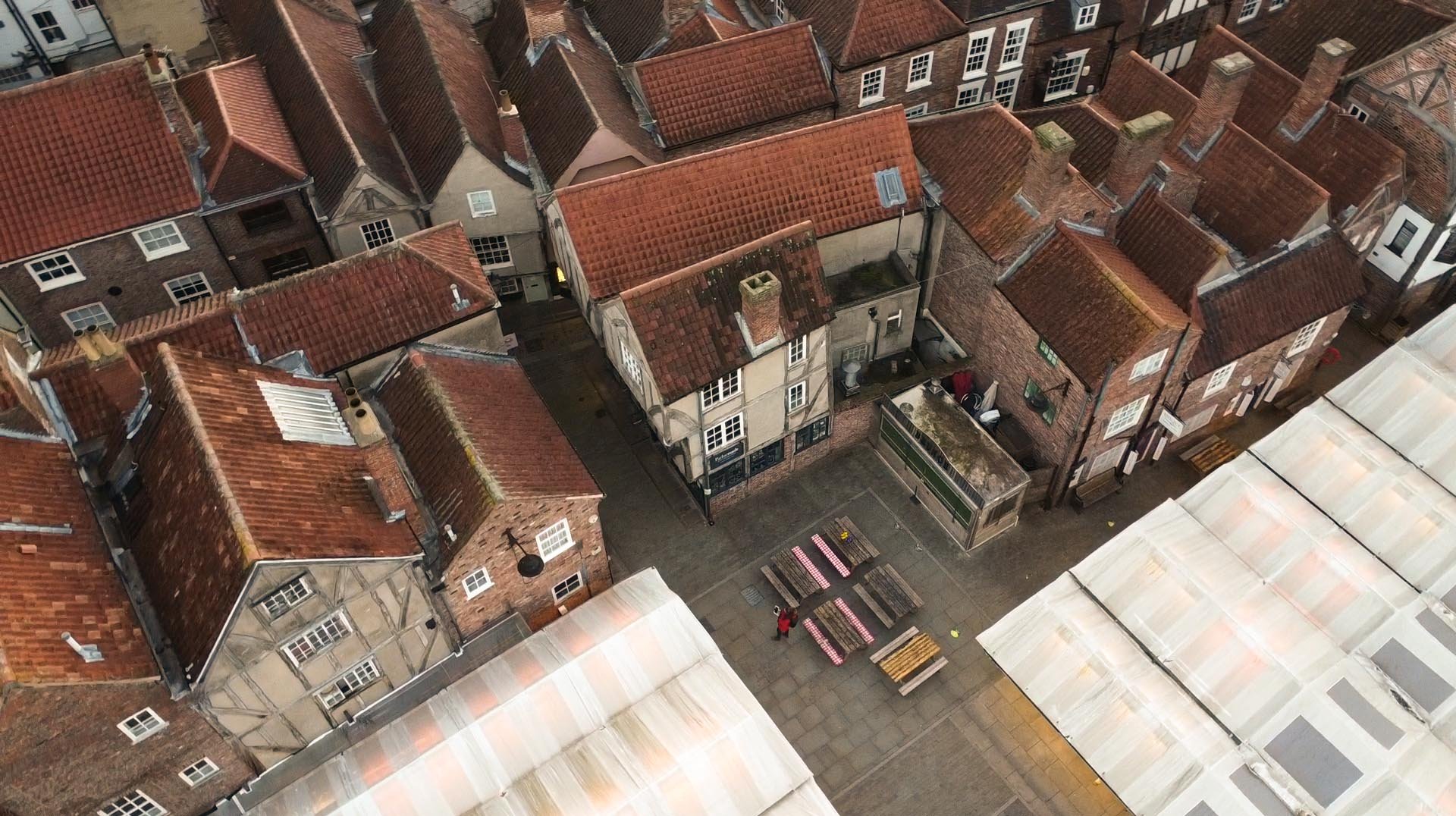
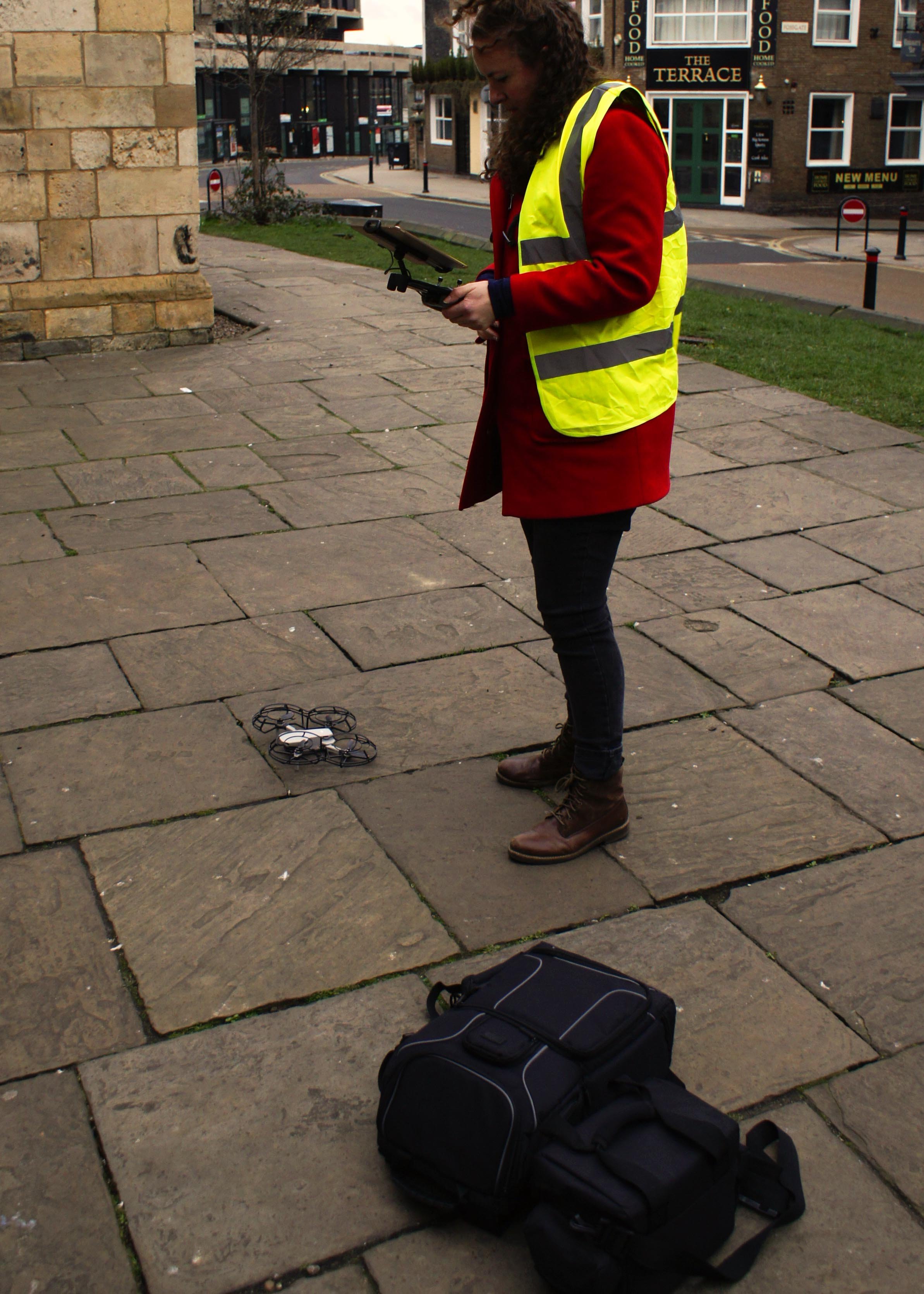
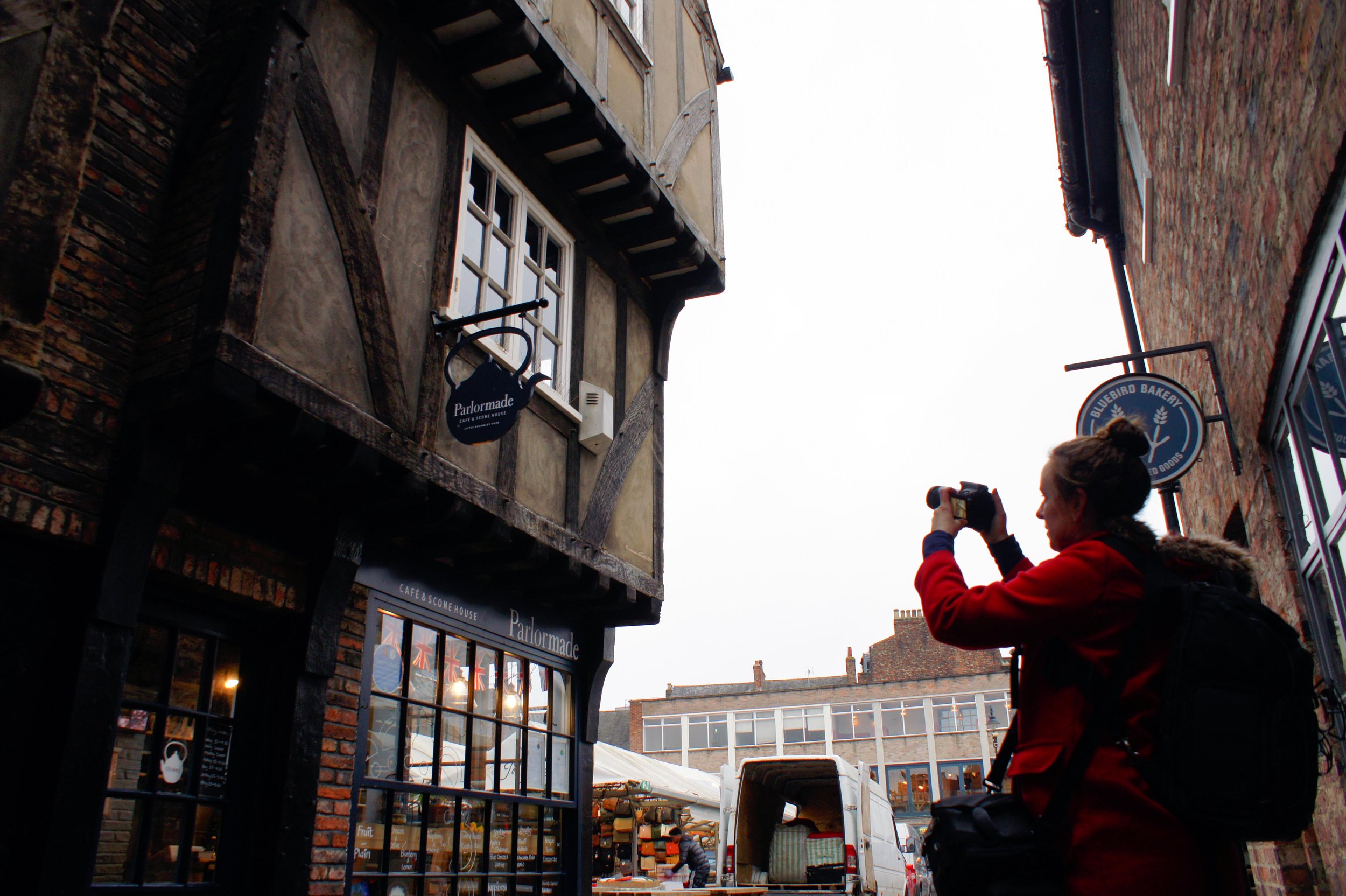
We broke the project into pieces, deciding to combine the exterior model and interior model in post. For the exterior, we took ground photography to try to get as much detail as possible, realizing that we’d not be able to get the angle we’d need to capture the roof without using a UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) because of how tightly packed the buildings are in the Shambles. Therefore, we used the drone to capture the upper angles of our building and those next to it. Because of the extreme difference between our ground angles and those from the drone, the software was not able to automatically combine these pictures into one model, so it required manual merging in 3DS Max. After much cleaning and post processing, we had the exterior completed and then shifted our focus on creating the interior.
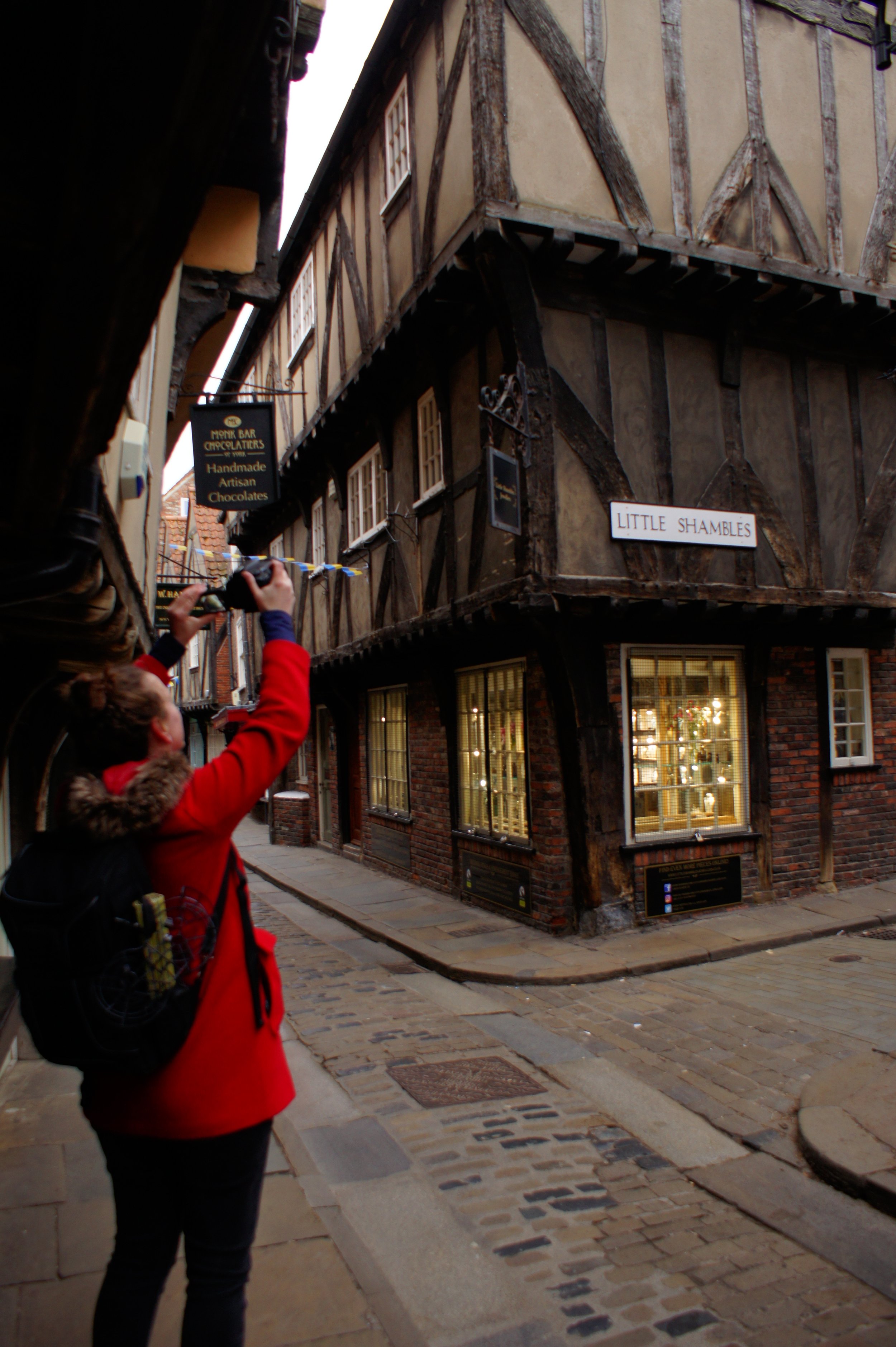
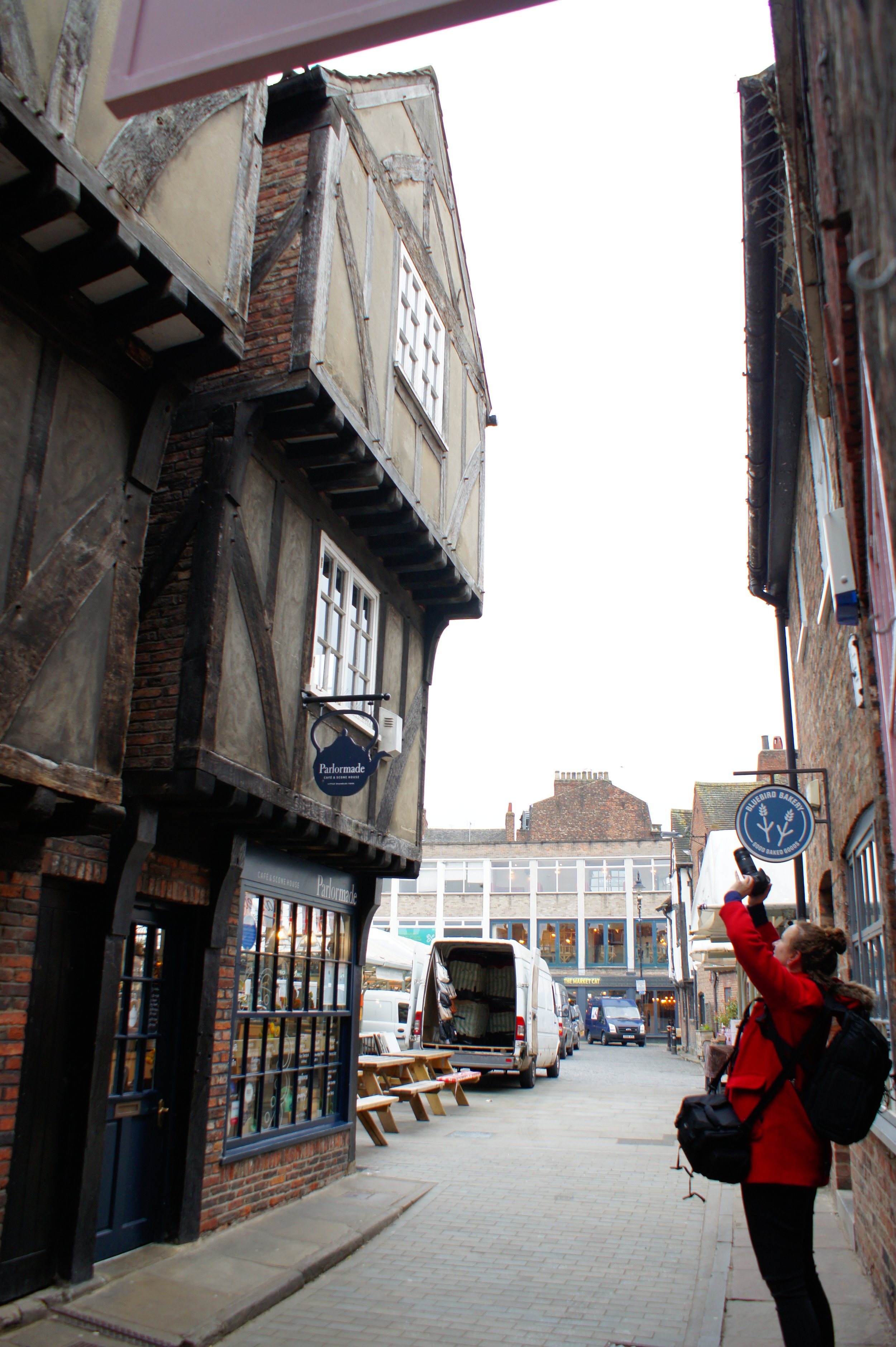
Creating photogrammetry models of interior spaces is more complicated than it may seem. Typically, in photogrammetry, you move in a circular path around your subject capturing it from all angles. However, when your subject surrounds you, in the case of a room, you have to change the way you think about capturing every surface. Our brilliant intern Ben, who is also a skilled photographer, did a large portion of the interior photography. He captured each wall as if it were its own ‘object’, but made sure to tie it to the adjacent wall through sufficient overlapping photography.
Blue squares represent the camera positions within the model.
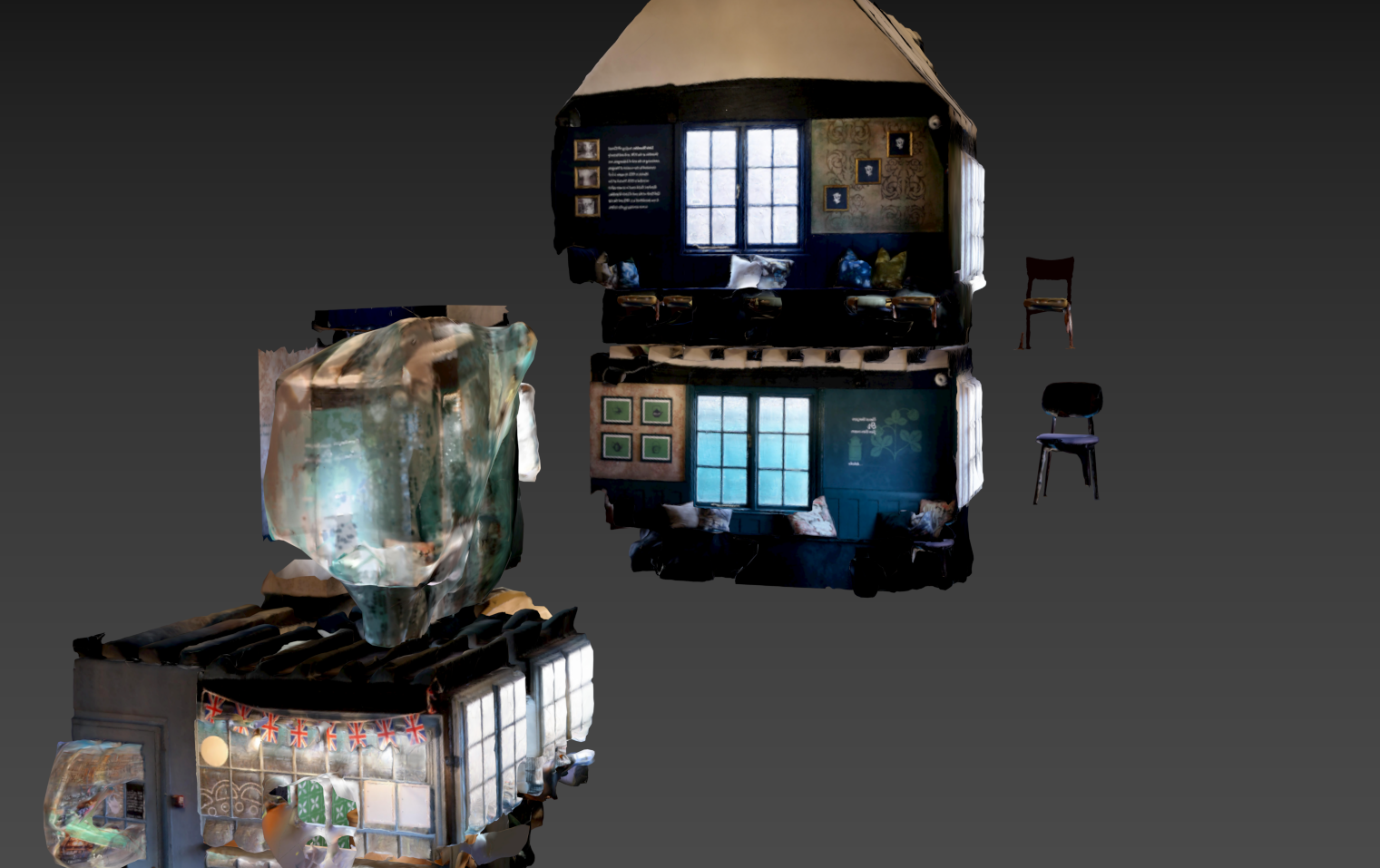
Piecing things together in post-production
However, some features will never do well, whether taken inside or out, and those are reflective surfaces like mirrors or windows. This is because the current software isn’t yet smart enough to figure out what a window is and how it should work when being modeled. Sunlight reflecting off surfaces like shiny wood can also cause distortion which is why a lot of the second floor chairs and table-tops needed a lot of reworking.
An amazing amount of information can be captured from the right photography. When looking at the second floor, you can see how well the high ceiling came out despite us not using a ladder to get closer shots, straight-on shots.
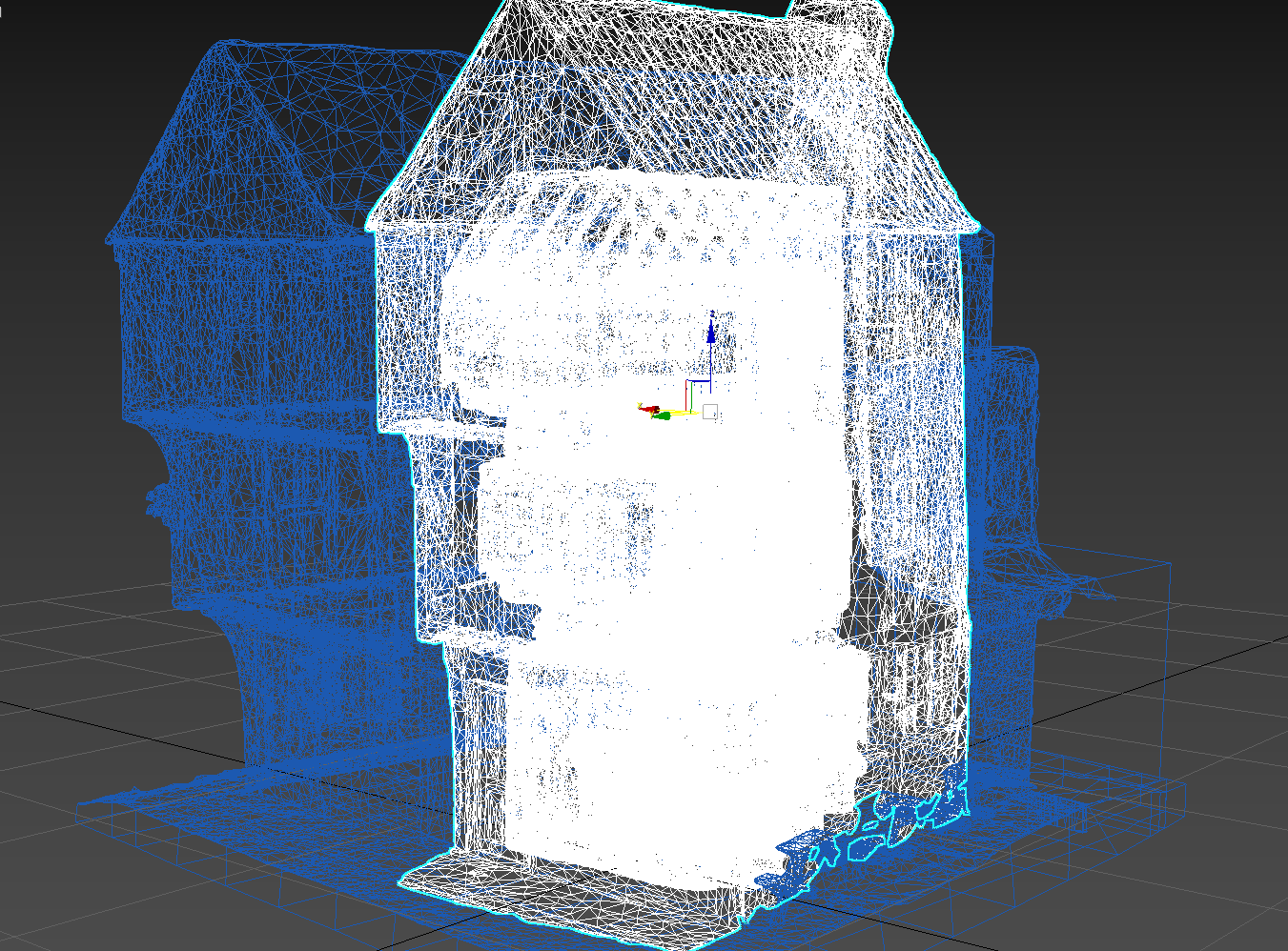
Wireframe of the completed model
The other complication with interior photogrammetry in a space like Parlormade is all the furniture that needs to be included and needs sufficient photographic coverage as well. Much of the building's internal features, such as the counter on the ground floor and the fireplaces, were captured easily enough. Features with spindly details like the chairs’ legs and the railing balusters did less well and had to be fixed in post. In fact, most of the chairs in the final model are a bit of a Frankenstein’s monster created by merging what was captured from different chairs into one jumble that resembles something somewhat realistic.
Though an attempt was made to cover each space thoroughly enough to be able to process all three floors into one model in the software, the challenge of narrow and dark staircases made this impossible. In the end, a lot of post processing work went into seamlessly merging different models into the single interior model for the final design.
Once the model was complete, it was uploaded to Sketchfab where customers/potential customers of Parlormade could view the building and move around it in the 3D viewer. We were asked to add some historical information to add context to the medieval structure. We completed a few days of research and came up with 10 ‘stops’ around the model to help viewers better understand the history of the building, the Shambles and the tea and scone industry in the UK. The final result acts like a virtual tour which users can view while enjoying a scone in the cafe or while sitting at home deciding where they’d like to visit. Through the Sketchfab platform, users can also utilise the VR viewing option for a fully immersive experience.
This project combined a lot of photography and planning with quite a bit of post processing in order to pull together an engaging and immersive model. The end result, with photo-realistic quality, gives users the ability to move around the space virtually and view each room from any angle.